Infra Led Yapısı :
29 Eylül 2010 Çarşamba
LED ve Infra Led Yapısı
Infra Led Yapısı :
İzleyiciler
TIMING CALCULATORS FOR THE LM555
TIMING CALCULATORS FOR THE LM555
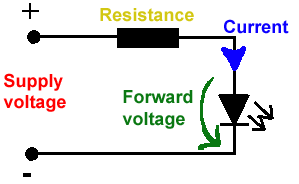
LED DİRENÇ HESAPLAMA
All LEDs require current limiting, without a current limiting mechanism the LED will usually burn out in under a second. Adding a simple resistor is the easiest way to limit the current. Use the calculator below to find out the value of resistor you require.
For example if you are wanting to power one of our_blank">red LEDs in an automotive application you would see that the typical forward voltage is 2.0 Volts and the maximum continuous forward current is 30mA. Therefore you would enter 14.5, 2.0 and 30 into the Single LED calculation box. After calculating you get 470ohm 1 watt as the result. Here is a that allows you to enter a resistor value and generate the corresponding color code.
Note: For automotive applications use the actual system voltage, not 12 Volts. Most 12 Volt system actually operate at around 14.5 Volts.
| Lm317 uygulama devreleri ve detayli bilgiye Buradan ulasabilirsiniz |
LM555 - ASTABLE OSCILLATOR CALCULATOR
NOTE: The leakage currents of electrolytic capacitors will affect the actual output results of the timers. To compensate for leakage it is often better to use a higher value capacitor and lower value resistances in the timer circuits.
LM555 Astable Oscillator Circuit Diagram
The next calculator can find the capacitance needed for a particular output frequency if the values of R1 and R2 are known.
| Value Of R1 Ohms | Value Of R2 Ohms |
| Frequency Desired Hertz |
|
| |
|
VOLT AMPER OHM ve WATT HESAPLAMA




Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder