| ADIN | Read on-chip analogue to digital converter. |
| ASM-ENDASM | It's always possible to insert assembly language. |
| BOX | Draw a square on a graphic LCD. |
| BRANCH | Computed GOTO for PIC devices with only one page memory. (= ONGOTO, see there) |
| BRANCHL | Computed GOTO for PIC devices with more than one page memory or 16-bit core PIC devices. (= ONGOTOL, see there) |
| BREAK | Exit a FOR-NEXT, REPEAT-UNTIL or WHILE-WEND loop early. |
| BSTART | Send a START condition to the I2C bus. |
| BSTOP | Send a STOP condition to the I2C bus. |
| BRESTART | Send a RESTART condition to the I2C bus. |
| BUSACK | Send a ACKNOWLEGDE condition to the I2C bus. |
| BUSIN | Read bytes from I2C device. |
| BUSOUT | Write bytes to I2C device. |
| BUTTON | Detect and debounce a key press. |
| CALL | Call assembly language subroutine. |
| CDATA | Define initial contents in memory. |
| CF_INIT | Initialise the lines used for Compact Flash card. |
| CF_SECTOR | Setup the sector in the Compact Flash card that is to be written or read by the commands CF_READ and CF_WRITE. |
| CF_READ | Read data from a Compact Flash card. |
| CF_WRITE | Write data to a Compact Flash card. |
| CIRCLE | Draw a circle on a graphic LCD. |
| CLEAR | Place a variable or bit in a low state or clear all RAM area. |
| CLEARBIT | Clear a bit or a port or variable, using a variable index. |
| CLS | Clear a LCD. |
| CONFIG | Adjust programming fuse configurations. |
| COUNTER | Count number of pulses on a pin. |
| CREAD | Read word from code memory. |
| CURSOR | Position the cursor on a LCD. |
| CWRITE | Write word to code memory. |
| DATA | Define initial contents in memory. |
| DEC | Variable = Variable - 1 (Decrement). |
| DECLARE | Adjust library routine parameters. |
| DELAYMS | Delay with millisecond resolution (ms). |
| DELAYUS | Delay with microsecond resolution (2s). |
| DEVICE | Choose the type of PIC to compile with. |
| DIG | Return the value of a decimal digit. |
| DIM | Create a variable. |
| DISABLE | DISABLE software interrupts that were previously ENABLED. |
| DTMFOUT | Produce a DTMF touch tone sequence on a pin. |
| EDATA | Define initial contents of on-chip EEPROM. |
| ENABLE | ENABLE software interrupts that were previously DISABLED. |
| END | Stop execution. |
| EREAD | Read byte, word or dword from on-chip EEPROM. |
| EWRITE | Write byte, word or dword to on-chip EEPROM. |
| FOR...TO...NEXT... STEP | Repeatedly execute statements. |
| FREQOUT | Generate one or two tones of differing or the same frequencies. |
| GETBIT | Examine a bit of a port or variable, using a variable index. |
| GOSUB | Call BASIC subroutine at specified label. |
| GOTO | Continue execution at specified label. |
| HBRESTART | Send a RESTART condition to the I2C bus using the MSSP module. |
| HBSTART | Send a START condition to the I2C bus using the MSSP module. |
| HBSTOP | Send a STOP condition to the I2C bus using the MSSP module. |
| HBUSACK | Send a ACKNOWLEDGE condition to the I2C bus using the MSSP module. |
| HBUSIN | Read bytes from I2C device using the MSSP module. |
| HBUSOUT | Write bytes to I2C device using the MSSP module. |
| HIGH | Make pin or port high. |
| HPWM | Generate a PWM signal using the CCP module. |
| HRSIN | Receive data from the serial port on devices that contain a USART. |
| HRSOUT | Transmit data to the serial port on devices that contain a USART. |
| HSERIN | Receive data from the serial port on devices that contain a USART. |
| HSEROUT | Transmit data to the serial port on devices that contain a USART. |
| HRSIN2 | Same as HRSIN but using a 2nd USART if available. |
| HRSOUT2 | Same as HRSOUT but using a 2nd USART if available. |
| HSERIN2 | Same as HSERIN but using a 2nd USART if available. |
| HSEROUT2 | Same as HSEROUT but using a 2nd USART if available. |
| IF...THEN...ELSEIF... ELSE...ENDIF | Conditionally execute statements. |
| INC | Variable = Variable + 1 (Increment) |
| INCLUDE | Load a BASIC file into the source code. |
| INKEY | Scan a matrix keypad. |
| INPUT | Make a pin or port an input. |
| LCDREAD | Read a single byte from a graphic LCD. |
| LCDWRITE | Write bytes to a graphic LCD. |
| LDATA | Place information into code memory. |
| LEFT$ | Extract n amount of characters from the left of a source string and copy them into a destination string. |
| LEN | Find the length of a string, NULL terminator not included. |
| [LET] | LET is optional (not necessary). Assign result of an expression to a variable. |
| LINE | Draw a straight line in any direction on a graphic LCD. |
| LINETO | Draw a straight line in any direction on a graphic LCD, starting from the previous LINE command's end position. |
| LOADBIT | Set or clear a bit of a port or variable, using a variable index. |
| LOOKDOWN | Search constant in table for value. |
| LOOKDOWNL | Search constant or variable in table for value. |
| LOOKUP | Fetch constant value from table. |
| LOOKUPL | Fetch constant or variable value from table. |
| LOW | Make pin or port low. |
| LREAD | Read a value from a LDATA table. |
| LREAD8 | Access 8-bit values from an LDATA table. |
| LREAD16 | Access 16-bit values from an LDATA table. |
| LREAD32 | Access 32-bit values from an LDATA table, this also includes floating point values. |
| MID$ | Extract n amount of characters from a source string beginning at n characters from the left, and copy them into a destination string. |
| ON GOSUB | Cause the program to Call a subroutine based on an index value |
| ON GOTO | Cause the program to jump to different locations based on a variable index. On a PICmicro device with only one page of memory. (See BRANCH) |
| ON GOTOL | Cause the program to jump to different locations based on a variable index. On a PICmicro device with more than one page of memory or 16-bit core devices. (See BRANCHL) |
| ON INTERRUPT | Execute a subroutine on a SOFTWARE interrupt. |
| ON_INTERRUPT | Execute a subroutine on a HARDWARE interrupt. |
| ON_LOW_INTERRUPT | Execute a subroutine when a LOW PRIORITY HARDWARE interrupt occurs on a 16-bit core device. |
| OUTPUT | Make a pin or port output. |
| OREAD | Receive data from a device using the Dallas 1-wire protocol. (One wire protocol) |
| ORG | Set program origin. |
| OWRITE | Transmits data to a device using the Dallas 1-wire protocol. (One wire protocol) |
| PAUSE | Better is using DELAYMS. |
| PEEK | Read byte from register. |
| PIXEL | Read a single pixel from a graphic LCD. |
| PLOT | Set a single pixel on a graphic LCD. |
| POKE | Write byte to register. |
| POP | Pull a single variable or multiple variables from a software stack |
| POT | Read potentiometer on a specified pin. |
| Display characters on a LCD. | |
| PULSIN | Measure pulse width on a pin. |
| PULSOUT | Generate pulse to a pin. |
| PUSH | Place a single variable or multiple variables onto a software stack. |
| PWM | Output pulse width modulated pulse train to a pin. |
| RANDOM | Generate a pseudo-random number. |
| RC5IN | Read infrared signal from Philips remote controls (TV, audio, etc.) (RC5 protocol) see also SONYIN. |
| RCIN | Measure pulse width on a pin. |
| READ | Read byte or word from memory. |
| REM | Add a remark to the source code, use as many text as you like. More clear is to use the apostrof (') or the point-comma (;) |
| REPEAT...UNTIL | Execute a block of instructions until a condition is true. |
| RESTORE | Adjust the position of data to READ. |
| RESUME | Re-enable software interrupts and return. |
| RETURN | Continue at statement following last GOSUB. |
| RIGHT$ | Extract n amount of characters from the right of a source string and copy them into a destination string. |
| RSIN | Asynchronous serial input from fixed pin and baud. |
| RSOUT | Asynchronous serial output to fixed pin and baud. |
| SEED | Seed the random number generator. |
| SELECT...CASE... ENDSELECT | Conditionally run blocks of code. |
| SERIN | Receive asynchronous serial data (i.e. RS232 data). |
| SEROUT | Transmit asynchronous serial data (i.e. RS232 data). |
| SERVO | Control a servo motor. |
| SET | Place a variable or pin in a high state. |
| SET_OSCCAL | Calibrate the on-chip oscillator. (Adjust intern oscillator) |
| SETBIT | Set a bit of a port or variable, using a variable index. |
| SHIN | Synchronous serial input (SHIFT IN). |
| SHOUT | Synchronous serial output (SHIFT OUT). |
| SLEEP | Power down processor for a period of time. |
| SNOOZE | Power down processor for short period of time. |
| SONYIN | Read infrared signal from Sony remote controls (TV, audio, etc.) (SIRC) see also RC5IN. |
| SOUND | Generate tone or white-noise on specified pin. |
| SOUND2 | Generate 2 tones to 2 separate pins. |
| STOP | Stop program execution. |
| STRN | Create a NULL terminated byte array. |
| STR$ | Convert the contents of a variable to a NULL terminated string. |
| SWAP | Exchange the values of two varibales. |
| SYMBOL | Create an alias for a variable or gives a name to a constant, port, pin or register. |
| TOGGLE | Reverse the state of a port bit. Makes an output high when it was low or low when it was high. |
| TOLOWER | Convert the characters from a source string to lower case. |
| TOUPPER | Convert the characters from a source string to upper case. |
| UNPLOT | Clear a single pixel on a graphic LCD. |
| USBINIT | Initialise the USB interrupt on devices that contain a USB module. |
| USBIN | Receive data via a USB endpoint on devices that contain USB. |
| USBOUT | Transmit data via a USB endpoint on devices that contain USB. |
| VAL | Convert a NULL terminated string to an integer value. |
| VARPTR | Locate the address of a variable. |
| WHILE...WEND | Execute statements while condition is true. |
| XIN | Receive data using the X10 protocol. |
| XOUT | Transmit data using the X10 protocol. |
27 Mayıs 2010 Perşembe
PIC Basic Komutlar Listesi
İzleyiciler
TIMING CALCULATORS FOR THE LM555
TIMING CALCULATORS FOR THE LM555
LED DİRENÇ HESAPLAMA
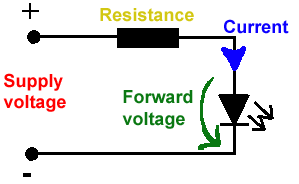
All LEDs require current limiting, without a current limiting mechanism the LED will usually burn out in under a second. Adding a simple resistor is the easiest way to limit the current. Use the calculator below to find out the value of resistor you require.
For example if you are wanting to power one of our_blank">red LEDs in an automotive application you would see that the typical forward voltage is 2.0 Volts and the maximum continuous forward current is 30mA. Therefore you would enter 14.5, 2.0 and 30 into the Single LED calculation box. After calculating you get 470ohm 1 watt as the result. Here is a that allows you to enter a resistor value and generate the corresponding color code.
Note: For automotive applications use the actual system voltage, not 12 Volts. Most 12 Volt system actually operate at around 14.5 Volts.
| Lm317 uygulama devreleri ve detayli bilgiye Buradan ulasabilirsiniz |
LM555 - ASTABLE OSCILLATOR CALCULATOR
NOTE: The leakage currents of electrolytic capacitors will affect the actual output results of the timers. To compensate for leakage it is often better to use a higher value capacitor and lower value resistances in the timer circuits.
LM555 Astable Oscillator Circuit Diagram
The next calculator can find the capacitance needed for a particular output frequency if the values of R1 and R2 are known.
| Value Of R1 Ohms | Value Of R2 Ohms |
| Frequency Desired Hertz |
|
| |
|
VOLT AMPER OHM ve WATT HESAPLAMA




Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder