22 Mart 2010 Pazartesi
ELEKTRONİK TE KULLANILAN KISALTMALAR
AC=Alternating Alternatif akım
AC/DC=Alternating current or Direct current Alternatif akım Doğru Akım
A/D=Analog to digital Analog dijital
ADC=Analog-to-digital Analog-dijital çevirici
AF=Audio frequency Ses frekansı
AFT=Automatic fine tuning Otomatik ince ayar
AFC=Automatic frequency Otomatik frekans kontrolü
AFC=Automatic flow controller controlling the flow of gasses under pressure into a vacuum Otomatik akış kontrolörü
AGC=Automatic gain control Otomatik kazanç kontrolü
Ah=Ampere hour Amper saat
Ai=Current gain Akım kazancı
AM=Amplitude modulation Genlik modülasyonu veya Frekans modülasyonu
AM/FM=Amplitude modulation or Frequency modulation AM/FM
AMM=Analog multimeter Analog multimetre
Antilog=Antilogarithm Antilogarithm
Ap=Power gain Güç Kazanmak
APC=Automatic phase control Otomatik Faz Kontrolü
Av=Voltage gain Gerilim Kazancı
AVC=Automatic volume control Otomatik ses kontrolü
AWG=American wire gauge Amerikan tel gauge
B=Flux density Akı yoğunluğu
Bfo=Beat frequency oscillator Beat frekans osilatör
BCD=Binary coded decimal Ikili kodlu ondalık
BJT=Bipolar junction transistor Bipolar Jonksiyonlu Transistör
BW=Bandwidth Bant Genişliği
c=Centi (10-2)
C=Capacitance capacitor Kapasitans veya kondansatör
CAD=Computer aided design Bilgisayar destekli tasarım
CAM=Computer aided manufacture Bilgisayar destekli üretim
CATV=Cablo tv
CB=Common base configuration Ortak temel yapılandırma
CB=Citizen's band Halk Bandı
CC=Common collector Ortak kolektör
CE=Common emitter Ortak emetör
Cm=Centimeter Santimetre
Cmil=Circular mil Dairesel mil
CPU=Central processing unit Merkezi işlem birimi
C(Q)=Coulomb Kulomb
CR=Junction diode Junction diyot
CRO=Cathode ray oscilloscope Katot ışın osiloskop
CRT=Cathode ray tube Katot ışınlı tüp
CT=Total capacitance Toplam kapasitans
Cw=Continuous transmission Sürekli iletim
D=Deci (10-1)
D/A or D-A=Digital to analog
DC=Direct current
Di or di=Change in current
DIP=Dual in-line package
DMM=Digital multimeter
DPDT=Double pole double throw
Dt or dt=Change in time
DTL=Diode transistor logic
Dv or dv=Change in voltage
DVM=Digital voltmeter
E=Instantaneous difference in potential
ECG=Electrocardiogram
ECL=Emitter coupled logic
EHF=Extremely high frequency
EHV=Extra high voltage
ELF=Extremely low frequency
EMF=Electromotive force
EMI=Electromagnetic interference
EW=Elektronic warfare
F=Frequency
FET=Field effect transistor
FF=Flıp Flop
Fil=Filament
FM=Frequency modulation
Fr=Frequency at resonance
Fsk=frequency-shift keying
FSD=Full scale deflection
G=Gravitational force
G=Conductance
G=Giga (10 9)
H=Henry
H=Magnetic field intensity
H=Magnetizing flux
H=hecto (102)
h=Hybrid
HF=High frequency
Hp=Horsepower
Hz=Hertz
I=Current
İ=Instantaneous current
IB=DC Base current
IC=DC Collector current
IC=Integrated circuit
Ie=Total emitter current
Ieff=;Effective current
IF=Intermediate frequency
Imax=Maximum current
Imin=Minimum current
I/O=input/output
IR=Infrared
I=Resistor current
IS=Secondary current
IT=Total current
JFET=junction field effect transistor
K=Coefficient of coupling
K=Kilo (103)
kHz=Kilohertz
kV=Kilovolt
kVA=Kilovoltampere
kW=Kilowatt
kWh=kilowatt-hour
L=Coil, inductance
LC=Inductance-capacitance
LCD=Liquid crystal display
L-C-R=Inductance-capacitance-resistance
LDR=Light-dependent resistor
LED=Light emitting diode
LF=Low frequency
LM=Mutual inductance
LNA=Low noise amplifier
LO=Local oscillator
LSI=Large scale integration
LT=Total inductance
M=Mega (106)
M=Mutual conductance
MI=Mutual inductance
M=Milli (10-3)
mA=Milliampere
Mag=Magnetron
Max=Maximum
MF=Medium frequency
mH=Millihenry
MHz=megahertz
Min=Minimum
Mm=Millimeter
Mmf=Magneto motive force
MOS=Metal oxide semiconductor
MOSFET=Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor
MPU=Microprocessor unit
MSI=Medium scale integrated circuit
mV=Millivolt
mW=Milliwatt
N=Number of turns in an inductor
N=Revolutions per minute
N=Nano (10-9)
N=Negative
nA=Nanoampere
NC=Normally closed
NC=No connection
NEG neg=Negative
nF=Nanofarad
nH=Nanohenry
Nm=Nanometer
NO=Normally open
NPN=Negative-positive-negative
Ns=Nanosecond
nW=Nanowatt
OP AMP=operational amplifier
P=Pico (10-12)
P=Power
P=Instantaneous power
P=Positive, also peak
PA=Public address or power amplifier
pA=picoampere
PAL=Programmable Array Logic
PAM pam=Pulse amplitude modulation
Pap=Apparent power
Pav=Average power
PCB=Printed circuit board
PCM pcm=Pulse-code modulation
PDM=Pulse-duration modulation
pF=Picofarad
PLD=Programmable Logic Device
PLL=Phase locked loop
PM=Phase modulation also Permanent magnet
PNP=Positive-negative-positive
POT, pot=potentiometer
P-P=Peak to peak
PPM=Pulse-position modulation
PRF=>Pulse repetition frequenc
PRT=Pulse repetition time
Pw=Pulse width
PWM, pwm=Pulse width modulatio
Q=Charge, also quality
Q=instantaneous charge
R=Potentiometer
R=Resistance
RAM=Random access memory
RC=Resistance-capacitance, also Radio controlled
Rcvr=Receiver
Rect=Rectifier
Ref=Reference
Rf=Radio frequencies
RF=Radio frequencies
RFI=Radio frequency interference
RL=Load resistor
RLC=Resistance-capacitance-inductance
RMS, rms=Root mean square
ROM=Read only memory
Rpm=Revolutions per minute
SCR=silicon controlled rectifier
SHF=Super high frequency
SIP=Single in-line package
SNR=Signal-to-noise ratio
SPDT=Single pole double throw sq
cm=Square centimeter
SSB=Single sideband
SW=short wave
SWR=Standing-wave ratio
SYNC sync=Synchronous
T=Tera (1012)
T=Torque
T=Transformer
T=Time in seconds
TC=Time constant, also temperature coefficient
TE=Transverse electric
Temp=Temperature
THz=Terahertz
TM=Transverse magnetic
TR=Transmit-receive
TTL=Transistor-transistor logic
TV=Television
TWT=Traveling wave tube
UHF=Ultra high frequency
UHV=Ultra high voltage
UJT=Unijunction transistor
UV=Ultraviolet Ultraviol
V=Vacuum tube Vakum tübü
V, v=Volt Volt
V=Instantaneous voltage Ani Voltaj
VA=Volt ampere voltaj Amper
Vav=Voltage (average value) Gerilim Ortalama değer
VBE=DC voltage base to emitter Beyz emiter için dc voltaj
V=Capacitive voltage Kapasitif gerilim
VCE=DC voltage collector to emitter Kollektör ve emitör için dc gerilim
VCO=Voltage controlled oscillator Gerilim kontrollü osilatör
VHF=Very high frequency Çok yüksek frekans
Vi=Input voltage Giriş gerilimi
VL=Inductive voltage Endüktif gerilim
VLF=Very low frequency Çok düşük frekans
Vm=Maximum voltage Maxsimum voltaj
VOM=Volt ohm milliameter Voltaj Ohm miliampermetre
Vout=Output voltage Çıkış voltajı
Vp=Primary voltage Birinci voltaj
VS=Source voltage Kaynak gerilimi
VSWR=Voltage standing wave ratio Gerilim duran dalga oranı
VT=Total voltage Toplam voltaj
W=Watt vatt
XC= Kapasitif reaktans
XL=Inductive reactance Endüktif reaktans
Y=Admittance Kabul giriş
Z=İmpedance
Zin=Input impedance Giriş empedansı
Zo=Output impedance Çıkış empedansı
Zp=Primary impedance Birinci empedans
Zs=Secondary impedance İkinci empedans
ZT=Total impedance Toplam empedans
İzleyiciler
TIMING CALCULATORS FOR THE LM555
TIMING CALCULATORS FOR THE LM555
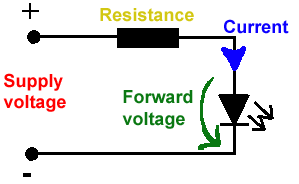
LED DİRENÇ HESAPLAMA
All LEDs require current limiting, without a current limiting mechanism the LED will usually burn out in under a second. Adding a simple resistor is the easiest way to limit the current. Use the calculator below to find out the value of resistor you require.
For example if you are wanting to power one of our_blank">red LEDs in an automotive application you would see that the typical forward voltage is 2.0 Volts and the maximum continuous forward current is 30mA. Therefore you would enter 14.5, 2.0 and 30 into the Single LED calculation box. After calculating you get 470ohm 1 watt as the result. Here is a that allows you to enter a resistor value and generate the corresponding color code.
Note: For automotive applications use the actual system voltage, not 12 Volts. Most 12 Volt system actually operate at around 14.5 Volts.
| Lm317 uygulama devreleri ve detayli bilgiye Buradan ulasabilirsiniz |
LM555 - ASTABLE OSCILLATOR CALCULATOR
NOTE: The leakage currents of electrolytic capacitors will affect the actual output results of the timers. To compensate for leakage it is often better to use a higher value capacitor and lower value resistances in the timer circuits.
LM555 Astable Oscillator Circuit Diagram
The next calculator can find the capacitance needed for a particular output frequency if the values of R1 and R2 are known.
| Value Of R1 Ohms | Value Of R2 Ohms |
| Frequency Desired Hertz |
|
| |
|
VOLT AMPER OHM ve WATT HESAPLAMA




Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder